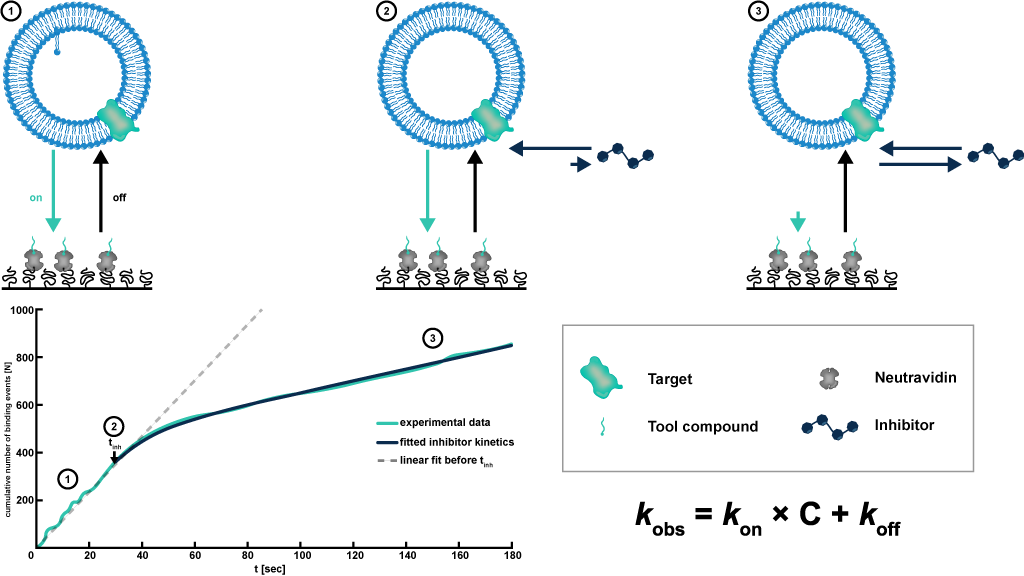
Unleashing the Potential of Membrane Protein Research with dISA
Membrane proteins play a vital role in drug discovery, as they are involved in various diseases and serve as potential therapeutic targets. However, studying membrane proteins presents unique challenges due to their complex nature. In recent years, a breakthrough technique called the Dynamic In-Solution Inhibition Assay (dISA) has emerged, offering a promising solution to overcome these challenges and unleash the full potential of membrane protein research.
Understanding the Significance of Membrane Proteins:
Membrane proteins reside within cell membranes and regulate critical cellular processes. They are involved in signaling, transport, and enzymatic functions, making them attractive targets for drug development. However, their unique characteristics, such as hydrophobicity and complex structural arrangements, pose significant challenges for researchers aiming to study their interactions and functionality.
The Limitations of Traditional Techniques:
Surface-based techniques like Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) have long been used to study drug-target interactions. However, when it comes to membrane proteins, these techniques encounter limitations. Immobilizing membrane proteins on surfaces is challenging, and the sensitivity and throughput of detection methods are often insufficient to capture their interactions accurately.
Introducing dISA: A Breakthrough Technique:
The Dynamic In-Solution Inhibition Assay (dISA) has revolutionized membrane protein research by offering a novel approach. Unlike surface-based techniques, dISA enables the study of membrane proteins in their native environment, allowing researchers to explore their interactions more accurately and effectively. By using solution-phase measurements, dISA overcomes the limitations of traditional techniques, providing a clearer understanding of membrane protein behavior.
Unveiling the Versatility of dISA:
dISA has wide-ranging applications in membrane protein research. It facilitates target identification, characterization, and screening processes. With dISA, researchers can measure kinetic parameters such as association and dissociation rates with high sensitivity, providing crucial insights into the interactions between membrane proteins and potential drug compounds. The versatility of dISA empowers researchers to delve deeper into membrane protein research and uncover new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Enabling Fragment-Based Drug Discovery (FBDD):
Fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) has gained significant attention in recent years. By using smaller compounds, known as fragments, researchers can explore a broader chemical space and identify potential lead compounds for drug development. However, detecting and characterizing fragment interactions with membrane proteins can be challenging. dISA offers a solution by facilitating fragment screening and enhancing the detection and analysis of fragment interactions, opening doors for innovative drug discovery approaches.
Future Perspectives and Impact:
The future of membrane protein research looks promising with the continued development and refinement of dISA technology. Ongoing advancements in dISA methodologies and equipment are expanding its capabilities and enabling researchers to tackle even more challenging membrane protein targets. By embracing dISA and other innovative techniques, scientists can accelerate the development of innovative therapies, improve patient outcomes, and make significant contributions to the field of drug discovery.
Conclusion:
The Dynamic In-Solution Inhibition Assay (dISA) has emerged as a game-changing technique in membrane protein research. By overcoming the limitations of traditional surface-based techniques, dISA enables researchers to unlock the potential of membrane protein research. Its versatility, accuracy, and ability to facilitate fragment-based drug discovery make dISA a valuable tool in the quest for novel therapeutics. By embracing dISA and harnessing its power, researchers can pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries, advancing the field of drug development and improving human health.